How Does Diabetes Affect the Body? Understanding the Impact on Health
Diabetes, a chronic condition that disrupts the body's ability to produce or use insulin, affects millions of people worldwide. This disease can lead to a cascade of health problems, ranging from heart disease and stroke to kidney failure and blindness.
Understanding how diabetes affects the body is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which diabetes can impact your health, from its effects on your organs to its long-term consequences.
Overview of Diabetes and Blood Sugar Levels
There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that occurs when the body's immune system destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Type 2 diabetes is more common and occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough insulin.
When you have diabetes, your blood sugar levels can fluctuate. If your blood sugar levels are too high, it's called hyperglycemia. If your blood sugar levels are too low, it's called hypoglycemia.
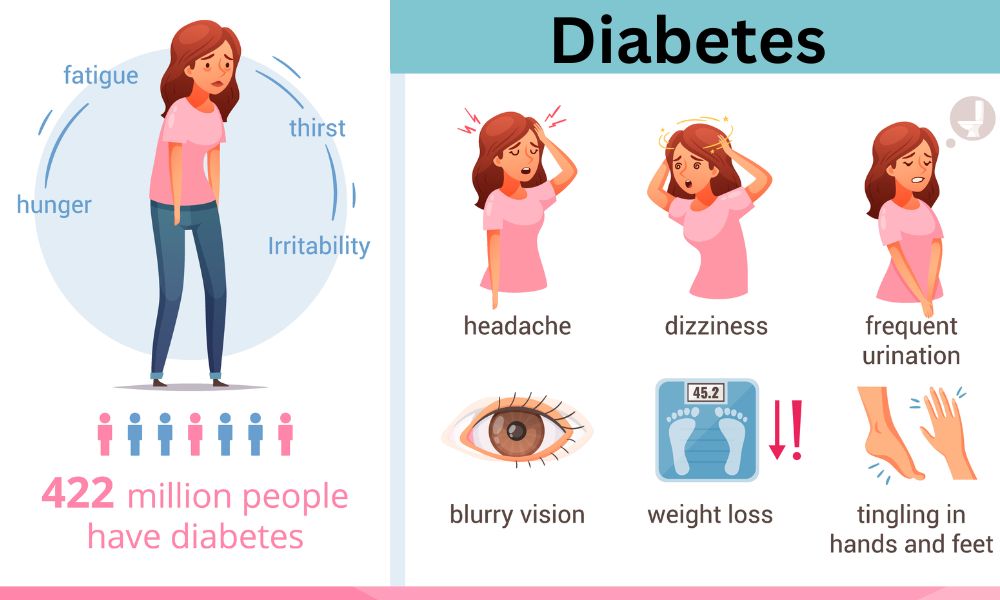
Symptoms of Too High Blood Sugar: Recognizing the Signs
High blood sugar can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Extreme hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
How Diabetes Effects on Your Body Systems
Diabetes can wreak havoc on your body, affecting multiple systems and organs. High blood sugar levels, a hallmark of diabetes, can damage blood vessels, nerves, kidneys, eyes, and other vital parts of your body. Such as,
1. Cardiovascular System: Increased Risk of Heart Disease
People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and lead to plaque buildup in the arteries.
2. Nervous System: Neuropathy and Nerve Damage
Diabetes can damage nerves throughout the body. This condition, called neuropathy, can cause numbness, tingling, pain, and weakness in the hands, feet, and other parts of the body.
3. Kidneys: Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetes can harm the kidneys, resulting in a condition known as diabetic nephropathy. Over time, diabetic nephropathy can lead to kidney failure.
4. Eyes: Diabetic Retinopathy and Vision Loss
Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina, and the back of the eye. This condition, called diabetic retinopathy, can lead to vision loss and even blindness.
5. Digestive System: Gastroparesis and Other Complications
Diabetes can cause gastroparesis, a condition that slows down the digestion of food. This may result in bloating, nausea, and vomiting.
How Does Diabetes Affect Your Organs?
Diabetes can also affect your organs in other ways, including:
Liver: Fatty Liver Disease
People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing fatty liver disease, a condition in which excess fat accumulates in the liver.
Skin: Wounds, Infections, and Skin Conditions
Diabetes can impair blood flow to the skin, making it more difficult for wounds to heal and increasing the risk of infections. Diabetes can also cause skin conditions such as acanthosis nigricans and fungal infections.
Pancreas: Insulin Production and Resistance Issues
In people with type 2 diabetes, the pancreas may produce less insulin or the body may become resistant to insulin. This can lead to high blood sugar levels.
Long-Term Effects of Diabetes on Your Body
Over time, diabetes can lead to a variety of chronic conditions, including:
1. Chronic Conditions Associated with Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Kidney disease
- Blindness
- Nerve damage
- Amputations
2. Managing and Mitigating the Effects of Diabetes
While diabetes is a chronic condition, there are ways to manage it and reduce your risk of complications. These include:
- Eating a healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Taking medication as prescribed
- Monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly
- Getting regular medical checkups
Conclusion: Preventing and Managing Diabetes Complications
Diabetes can have a significant impact on your health. However, by taking steps to manage your diabetes, you can reduce your risk of complications and improve your quality of life.







